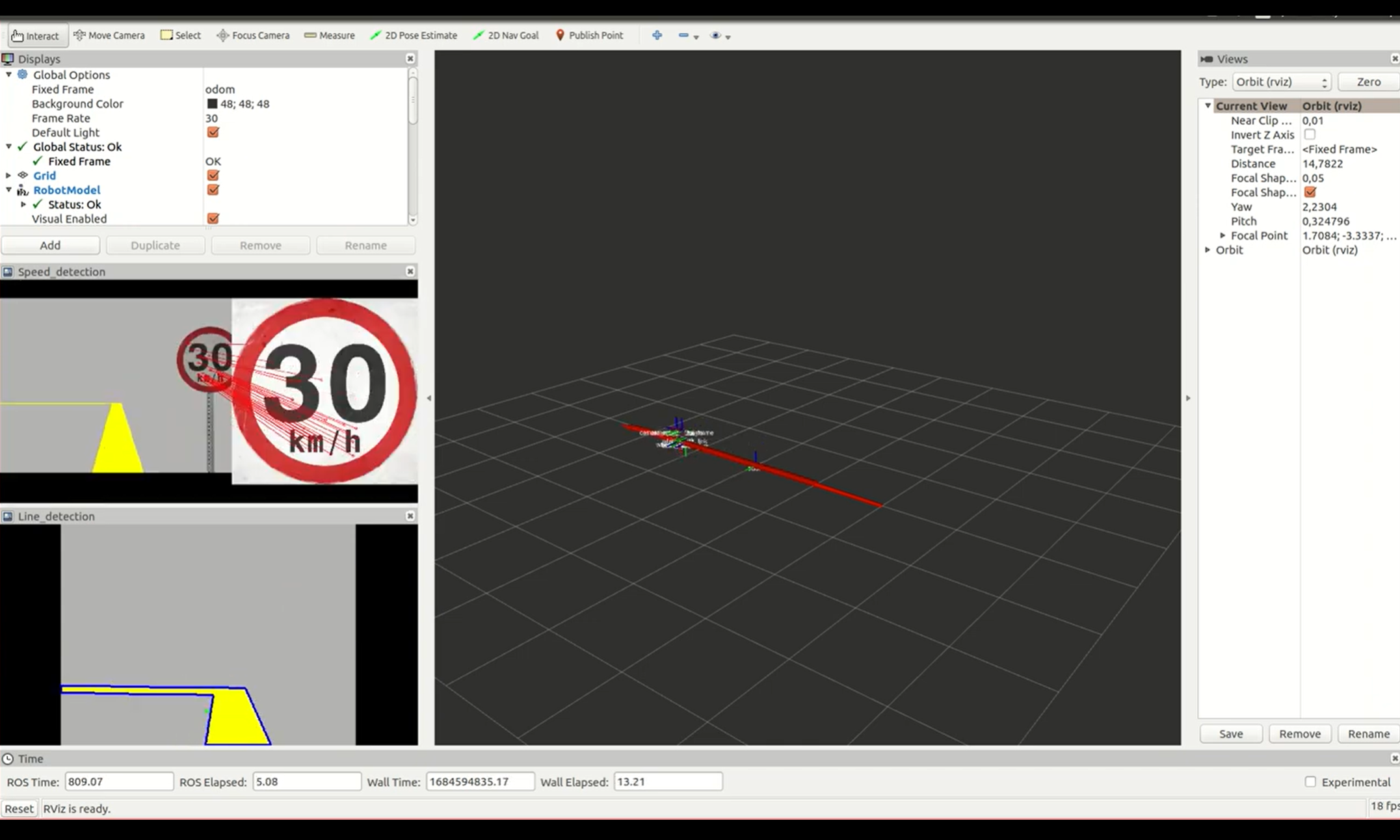
Line following with speed limit sign detection
May 2023 »Intro
Goal
Autonomous navigation of Turtlebot3 with RGB camera (pi camera)
- Follow the yellow line on the ground.
- Detect speed limit sign aside.
- Adjust speed according to the speed limit.
- Stop when reaching the end of yellow line.
Structure Overview
Main nodes:
- speed_detect: given 3D position of target object, generate motion command to chase after it.
- Subscribes to
'/camera/rgb/image_raw'(sensor_msgs/Image) - Publishes to
'/image_result'(sensor_msgs/Image): visualizing the sign detection result - Publishes to
'speed_limit'(std_msgs/Float32)
- Subscribes to
- line_follower: object detection & obtain its 3D position.
- Subscribes to
'/camera/rgb/image_raw'(sensor_msgs/Image) - Subscribes to
/speed_limit(std_msgs/Float32): the detected speed limit - Publishes
/image_line(sensor_msgs/Image): visualizing the line detection result - Publisher
/cmd_vel(geometry_msgs/Twist): control the velocity of turtlebot
- Subscribes to

1. Simulation world preparation
World file
Components
Turtlebot_burger_pi
Utilized the robot description of turtlebot3_burger_pi, which is from the turtlebot3_description package in turtlebot3.
$ git clone https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3.git
The urdf in this project is a modified version of the original turtlebot3_burger_pi.gazebo.xacro file. The camera parameters are adjusted in order to be more suitable under this gazebo environment.
Speed limit sign
There exists a speed limit sign model, showing a speed limit of 16 km/hr, in gazebo. To generate the sign with different speed limit value, copy the 'speed_limit_sign' folder. Then,
- change the image source in the
/meshes/speed_limit_sign.dae - change the model name to
speed_limit_sign_$(val)inmodel.config&model.sdf
Speed limit signs with value: 16, 30, 40, 50, 110 are avaliable at models. Copy those models to the directory where all the other gazebo models are stored.
In the final world environment, I also rescaled the signs to make them more compatible with the scale of yellow lines. This is done by adjusting the
Yellow line on the ground
Made use of the lfm.world from Line_follower_turtlebot. The world has a room and yellow path within.
For simplicity, I removed the room and add those speed limit signs along the path.
2. Speed limit sign detection
Implemention
Implemented in speed_detect.py
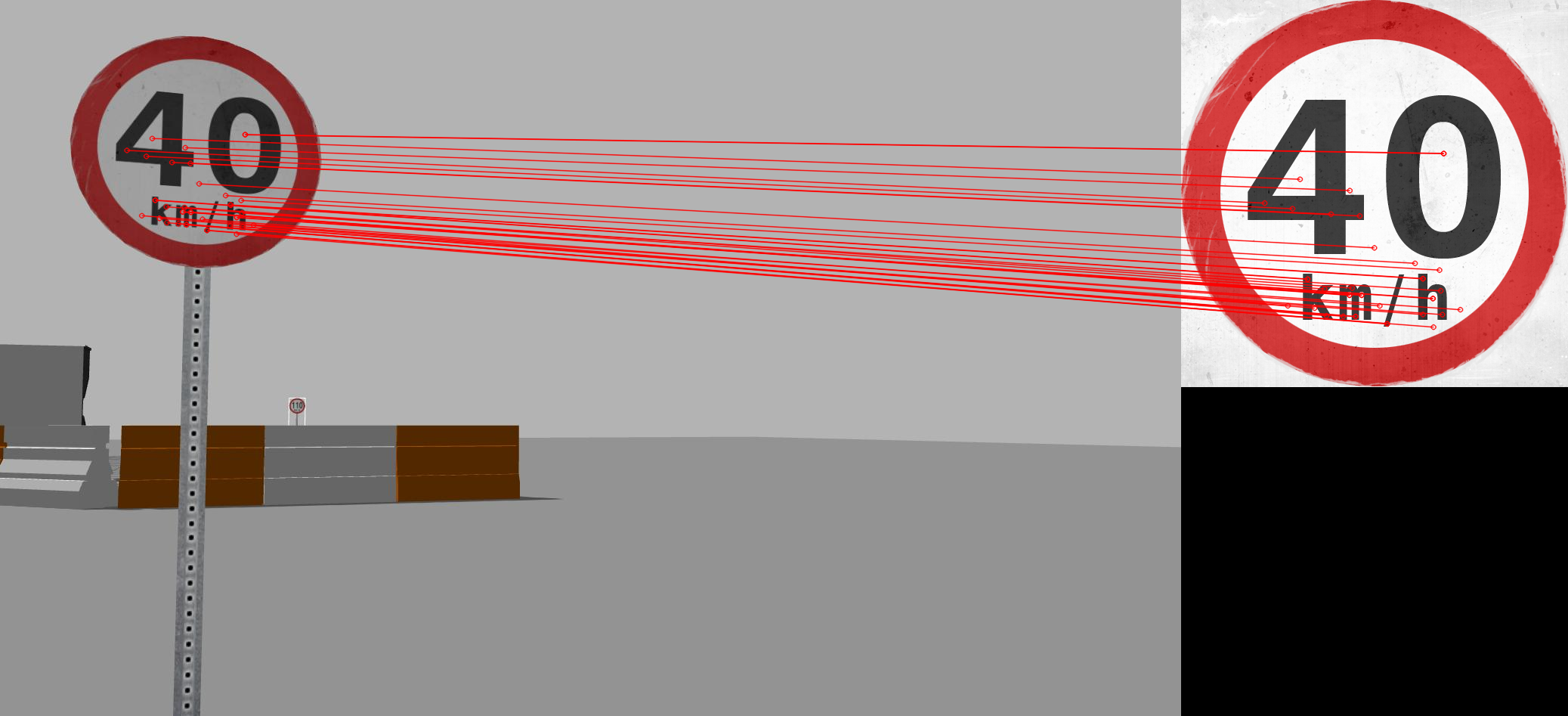
The detection is based on SIFT features matching. Speed sign image files (in gazebo model - speed_limit_sign/materials/textures) are served as templates. The SIFT features of all templates would be recomputed and stored.
For each camera image input, compute its SIFT features, then brute-force matching with all templates. The best match would be the speed detection result, and the value read would be published.
Components
SIFT features
SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) identify local keypoints and descriptor, describing the keypoint in a higher-dimensional feature space.
To compute SIFT feature of the camera BGR image
# Create instance of SIFT detector
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
# Convert to grayscale image
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Compute SIFT features
keypoints, descriptors = sift.detectAndCompute(img_gray, None)
Flann-based matching
FLANN (Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors) performs efficient feature matching (i.e., matching the keypoint descriptors) between images.
# Instantiate FlannBasedMatcher
index_params = dict(algorithm=0, trees=5)
search_params = dict(checks=100)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params, search_params)
# Match the descriptors of input image & template image
# i.e., descriptors (input image), descriptors_temp (template image)
matches = flann.knnMatch(descriptors, descriptors_temp, k=2)
good_match = []
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.7 * n.distance:
good_match.append(m)
if len(good_match) > min_match_threshold:
# Determined as a valid match ....
Detection result visualization
3. Line following
Implementation
Implemented in line_follower.py
Components
Image processing
Input: BGR image
- Gaussian blur
- Convert to HSV
- HSV thresholding, capturing only the yellow region
- Find contours in masked image. The largest contour would be treated as the yellow path.
- Compute the mass center of the line.
Generate velocity command
Adjust angular velocity based on line centroid. Try to tilt its orientation to keep the centroid at the center of camera view.
Note that, based on this implementation, the turtlebot would not follow exactly the path at the corner and would have some deviation. The reason is that, the yellow path after the corner would also be detected and would shift the position of the centroid, hence the turtlebot would slowly drift to the direction before the 90 degree turn.
If it is required to follow exactly the yellow path, then one may need to create a bounding region, perhaps a rectangle region in the front, so that it would only look at the path on the front and would not be affected by the path afterwards.
As for the linear velocity, if ros parameter use_speed_limit in the launch file is set as false, then it would go at a constant speed. If it is set as true, then it would be adjusted based on the detected speed limit value.
Detection result visualization
The contour of yellow line is visualized in blue color, and the centroid of it is visualized as the green point.
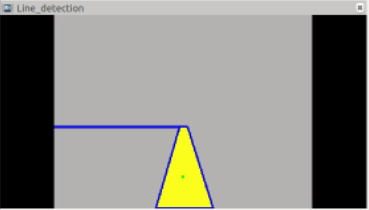
Final result
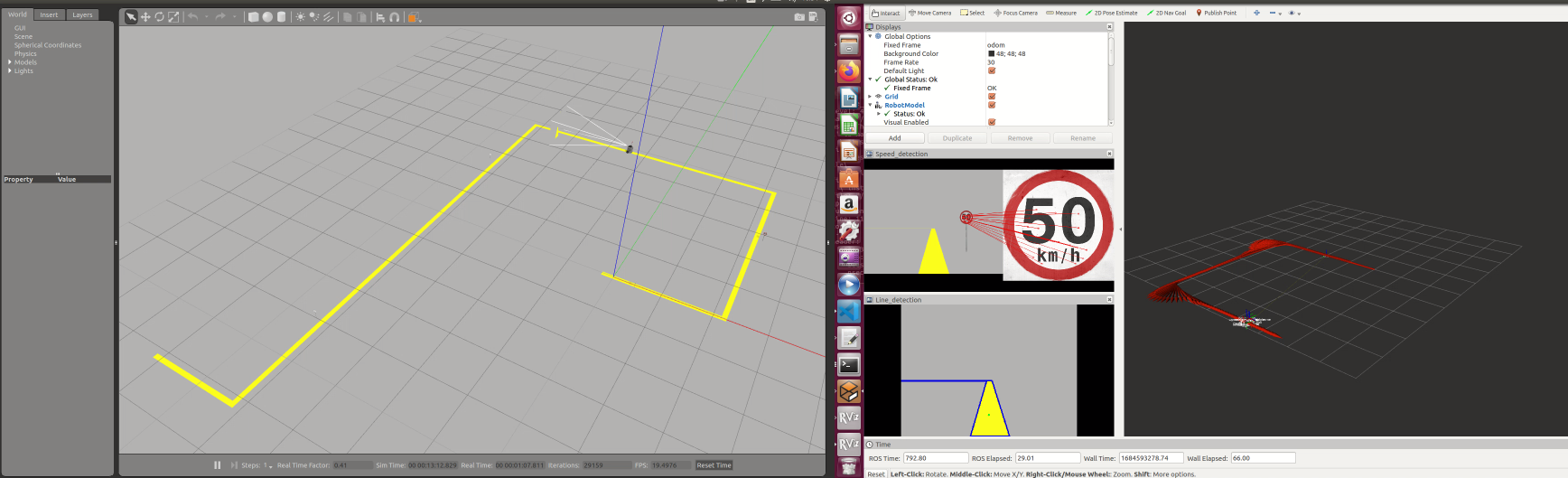
Video
(There is some latency due to the heaving computation loading. The actual process runs much smoother.)
Summary
- The choice of using flann-based matching of SIFT features is based on trial-and-error with different methods. Considering in real-world scenarios, signs could have different colors or different formats, and the signs could appear at different scales. Hence, a robust detection under different lightings and is scale-invariant is targeted. Other common street signs could also be detected as long as the template image is added to the template database.
- The line detection is based on color detection. Further improvement would be limiting the detecting area so that the robot would only focus on the path ahead, but it may require some deceleration before turning.
- Further TODO:
- work with tracks with two lines on the side (ex: the turtlebot autorace track).
- try out other detection methods.
Reference
- turtlebot3_autorace_simulation
- Line_follower_turtlebot
- SIFT features
- https://www.thepythoncode.com/article/sift-feature-extraction-using-opencv-in-python
- https://medium.com/data-breach/introduction-to-sift-scale-invariant-feature-transform-65d7f3a72d40
- FLANN-based matching
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-opencv-flannbasedmatcher-function/
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/how-to-implement-flann-based-feature-matching-in-opencv-python